Basic
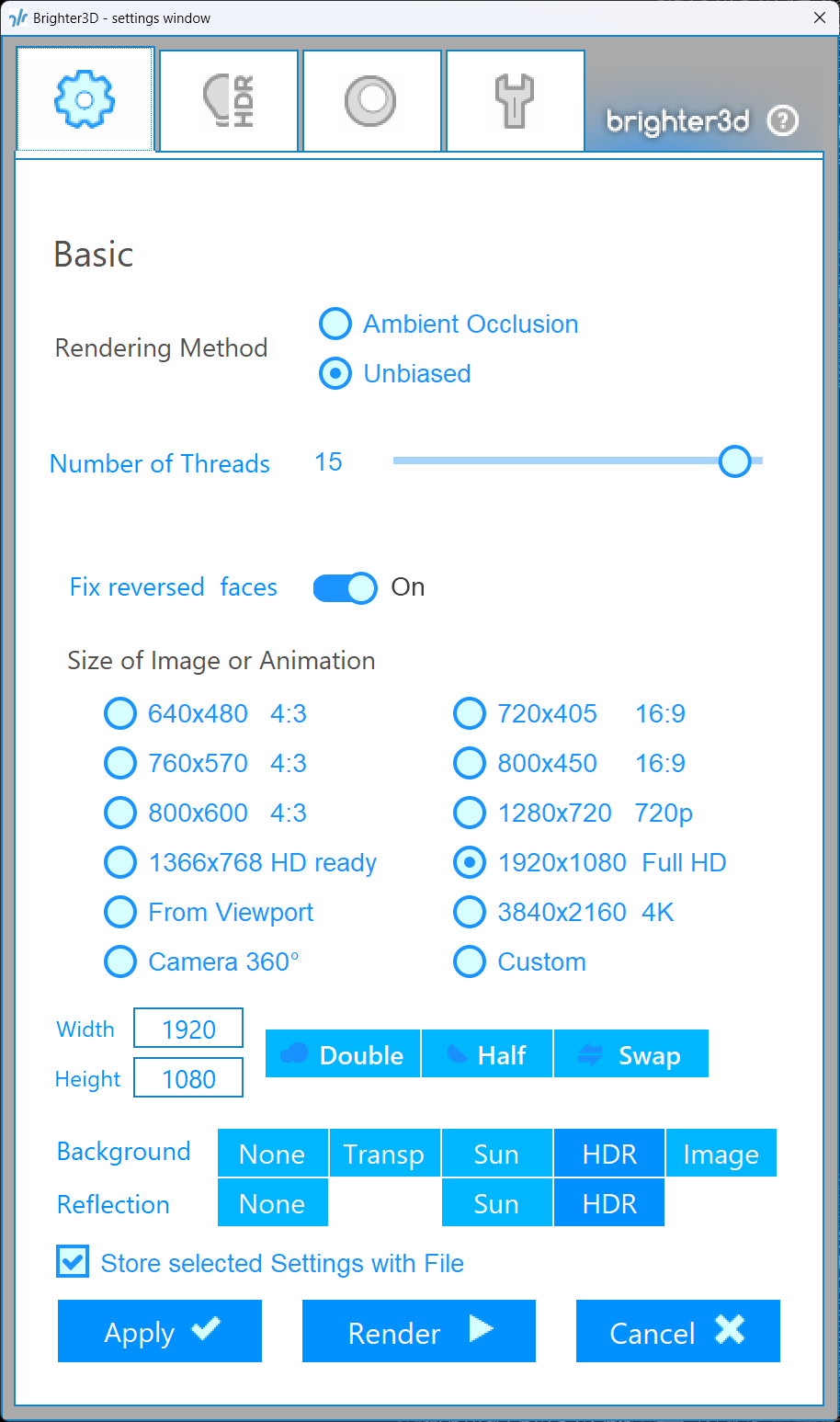
- 1 Ambient Occlusion is the simplest and fastest rendering mode. It does not require any light setup, making it ideal for quick previews or scenes where lighting complexity is minimal. This mode simulates soft, indirect lighting to enhance depth and realism in shadowed areas. It can be combined with daylight for more dynamic results
- 2 Unbiased is a high-quality rendering mode that iteratively refines the image to converge on a physically accurate result. This mode is computationally intensive but produces realistic lighting, shadows, and reflections based on real-world physics
- 3 Number of Threads This setting determines the number of CPU threads allocated to the rendering process. The recommended value is the number of logical CPU cores minus one. For example, if your system has 8 logical cores, set this to 7 to reserve one core for other system tasks, preventing slowdowns or unresponsiveness during rendering.
- 4 Fix reversed faces option attempts to automatically correct flipped faces (normals pointing in the wrong direction) during ray tracing. This is useful for ensuring proper geometry rendering in most materials. However, this feature does not work reliably for transparent materials like glass. In such cases, you must manually correct the face orientation in SketchUp
- 5 Preset resolutions option allows you to select from predefined image resolution presets for your rendered output. Common resolutions include standard sizes like 1920x1080 (Full HD), 1280x720 (HD), or 3840x2160 (4K)
- 6 From Viewport option sets the rendered image resolution to match the current viewport size in SketchUp. This ensures that the render matches the exact framing and composition seen in the viewport
- 7 360° Camera mode renders equirectangular images, which are ideal for creating high-dynamic-range (HDR) maps used in lighting setups or for viewing in 360-degree virtual reality (VR) applications. This mode captures a full spherical view of the scene
- 8 Custom This option allows you to manually specify the width and height of the rendered image, offering full control over the output resolution.
- 9 Width Width of the rendered image in pixels. This value determines the horizontal resolution of the output.
- 10 Height Height of the rendered image in pixels. This value determines the vertical resolution of the output.
- 11 Double doubles both the width and height of the current resolution, effectively quadrupling the total pixel count (e.g., a 1920x1080 image becomes 3840x2160). This increases image detail but significantly increases rendering time
- 12 Half halves both the width and height of the current resolution, reducing the total pixel count to one-quarter of the original (e.g., a 1920x1080 image becomes 960x540). This reduces rendering time at the cost of lower image detail
- 13 Swap This option swaps the width and height values of the image resolution, effectively rotating the aspect ratio (e.g., a 1920x1080 image becomes 1080x1920). This is useful for changing between landscape and portrait orientations
- 14 Background selection determines what appears behind your 3D scene in the render. The available options are:
None Renders the background as solid black. Useful for isolating the model or when a background is not needed.
Transparent Saves the background as transparent when exporting to formats like PNG that support alpha channels. Ideal for compositing the render into other images or videos.
Sun Uses a daylight background, simulating natural outdoor lighting. Best for scenes that require a realistic sky or sunlight.
HDR Uses an HDR or EXR map as the background, providing high-fidelity lighting and reflections. Ideal for professional visualizations or scenes requiring complex lighting.
Image Uses a user-specified JPEG or PNG image as the background. Useful for custom backdrops or matching specific environments.
- 15 Reflection selection determines the environment used for reflections on reflective surfaces in your scene. The available options are:
None No reflections are rendered on surfaces, resulting in a flat appearance for reflective materials.
Sun Uses a daylight map to generate realistic reflections, simulating natural outdoor lighting.
HDR Uses an HDR or EXR map to create detailed and realistic reflections, ideal for high-quality visualizations.